![]()
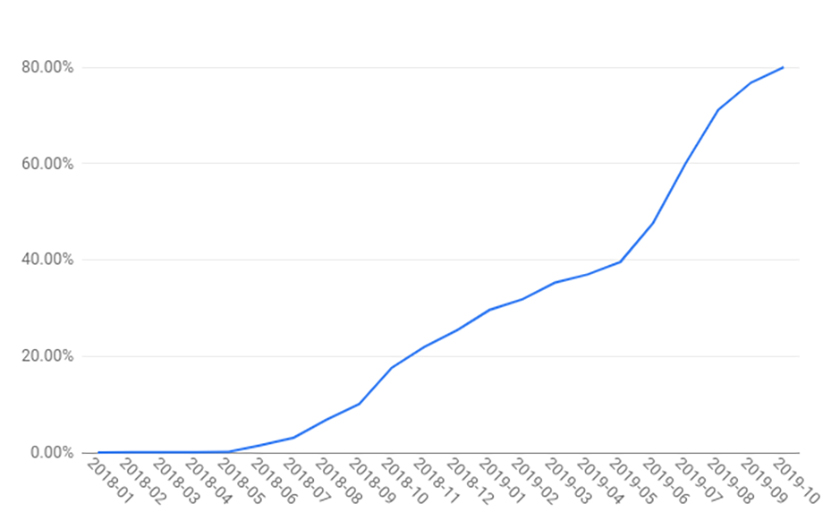
Today, Google revealed some new information pertaining to Android app encryption. According to Google's data, 80% of Android apps available on the Google Play Store now have network encryption enabled by default.
What does that mean? That means that when an app requests or sends information from your phone over a network, all that information is encrypted with Transport Layer Security (TLS). This helps keep your information safe.
The fact that default Android app encryption is now at 80% is terrific news. It's even more impressive when you take a look at the graph below, which shows the percentage over time of apps that are encrypted by default:
 Google
Google
As you can see, Android app encryption by default was at about 0% at the beginning of 2018, so we've come quite a long way.
Going forward, Google only sees this statistic increasing. Any Android app targeting Android 9 Pie or higher must have TLS encryption enabled by default. Starting on November 1, 2019, all Android apps (and Android updates) must target Android 9 Pie, so app encryption percentages will only increase.
Related: How does encryption work? Gary explains.
As good as this Android app encryption news is to hear, that still means that 20% of Android apps do not enable encryption by default. There are about 2.8 million apps on the Google Play Store, which means around 560,000 of those apps send and receive unencrypted information. That's a lot of apps that you could potentially have on your phone right now.
This is a good reminder to make sure you are always using the latest version of an application and that you don't rely too heavily on older, outdated apps.
More posts about Android Apps
from Android Authority https://ift.tt/33Q7IBX
via IFTTT










No comments:
Post a Comment